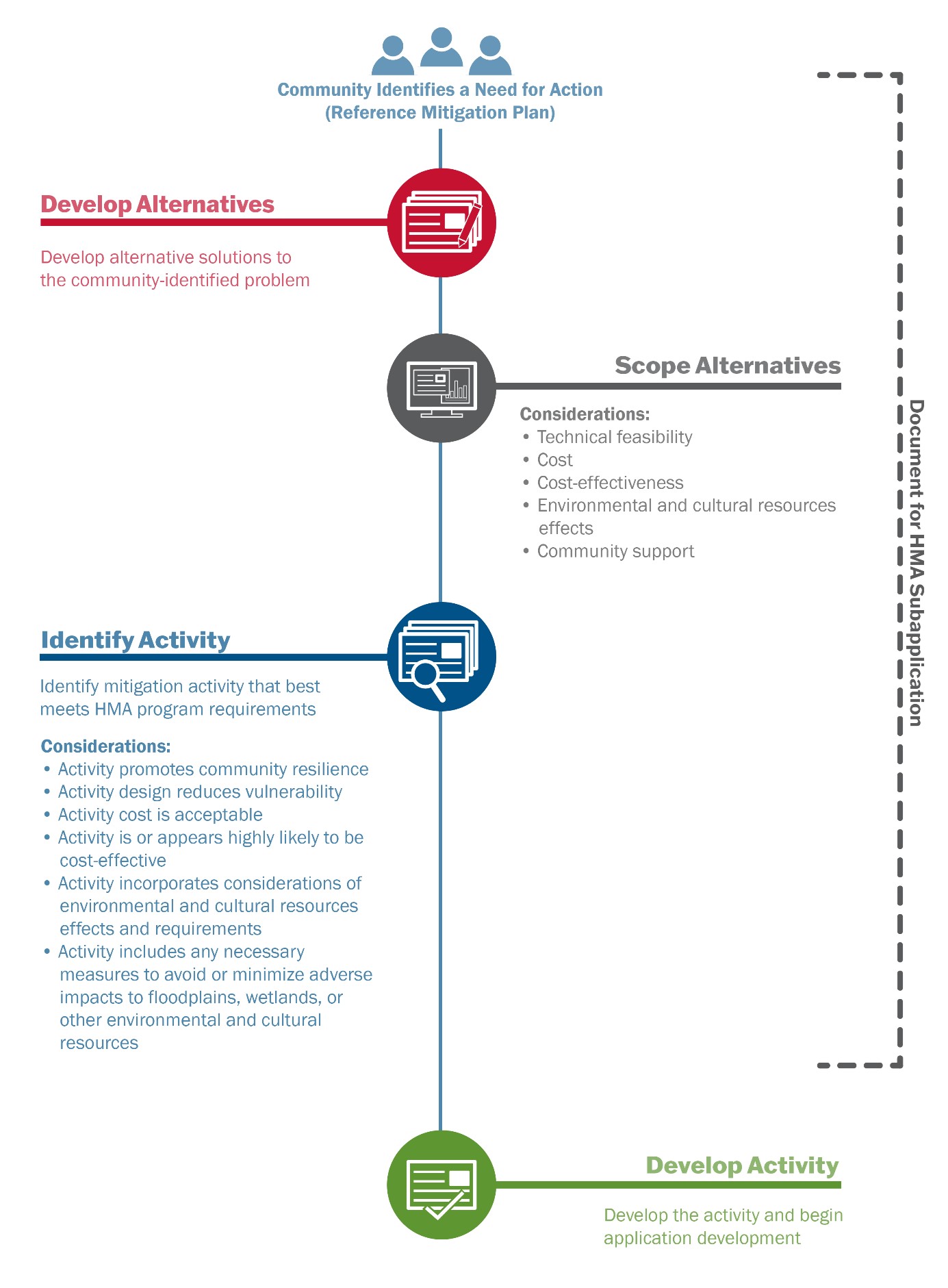
Scoping can significantly impact the course an application or subapplication takes through the HMA process. Scoping is the process by which subapplicants evaluate and select a preferred mitigation alternative and develop a detailed outline of all aspects of the activity, including goals, all related activities, resources, timelines and deliverables, as well as the activity’s boundaries.
The scoping process may include, depending on the activity type, an evaluation of technical feasibility, cost review, cost-effectiveness, as well as EHP or cultural resource considerations of the mitigation alternatives. Other considerations may include climate change impacts and racial equity. The scoping process results in the development of a preferred activity alternative that is then documented through the preparation of the application or subapplication.
Eligible applicants and subapplicants that actively participate in and document the scoping process put themselves in a greater position for success during subapplication development. The information gathered in the scoping process serves as the basis for the development of a more detailed and robust scope of work, budget and EHP compliance components of the mitigation activity.
During the scoping process, the applicant and subapplicant may encounter considerations such as technical feasibility, cost-effectiveness and EHP requirements that necessitate the refinement or adjustment of the mitigation activity. In these situations, the reason for the refinement or re-scoping should be fully documented and included with the subapplication. Figure 3 details considerations during each step of the scoping process.
Applicants and subapplicants should consider the whole range of program requirements at the beginning stages of activity scoping. Addressing HMA program requirements at the earliest stage possible in the decision-making process is important because it can lead to enhanced project scoping and development as well as prevent delays later in the subaward lifecycle.
The HMA program requirements comprise the following topics:
- Hazard mitigation plan requirements.
- Technical feasibility and effectiveness.
- Floodplain management and protection of wetlands.
- EHP review and compliance.
- Cost-effectiveness.
- Cost review.
For specific information on scoping local hazard mitigation plans, refer to the Considerations for Local Mitigation Planning Grant Subapplications FEMA job aid (March 2021). For specific information on scoping tribal hazard mitigation plans, refer to the Tribal Mitigation Planning and HMA Grant Application Development FEMA job aid (March 2021).