Earth Day highlights the power of community and the collective progress that can be achieved when people come together to provide environmental solutions for everyone to live, work and play. FEMA commits to supporting communities in this effort by investing in sustainable and equitable solutions to meet the growing environmental needs of communities around the nation — a step towards building a better tomorrow.
FEMA actively works toward these goals by providing numerous grant opportunities, extending disaster assistance and improving accessible agency resources, policies and programs. The agency also develops innovative tools that help increase climate awareness so that communities can better understand their climate-related hazard risks and how to prepare for them.
FEMA’s Resilience Programs help communities build their capacity to withstand hazards, recover from disasters and thrive in the aftermath. By focusing on resilient solutions, communities can be prepared for natural disasters, speed up recovery and reduce suffering — particularly critical for communities at higher risk or who are disproportionately impacted.
Natural disasters often disproportionately impact people in underserved communities where weakened infrastructure, fewer resources and less support to invest in hazard mitigation can make disasters more challenging. By improving and increasing solutions for the most vulnerable communities and their needs, we create safe environments and climate resilience for everyone.
Climate-related hazards such as floods, hurricanes, wildfires, droughts and severe heat are increasing frequently. Since 2019, the United States has experienced at least 20 natural disasters annually, causing approximately 400 deaths per year, with disaster losses exceeding $1 billion each. Within 2023, 28 natural disasters occurred, with losses exceeding a total of $93 billion. The growing severity of disasters can impact the time it takes communities to recover — a process that can be complicated by repetitive natural disasters in areas already struggling to bounce back.
The agency focuses on building community resilience and improving environmental justice through its close collaboration with federal, state, local, Tribal Nations and territorial governments, community-based organizations and the private sector to provide solutions and target equitable investments to create a more resilient nation.

Below are some ways FEMA is working toward these goals.
1 - Investing in Climate Mitigation
FEMA dedicated nearly $3 billion in climate resilience funding, including $1.8 billion for critical resilience project funding by the Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) program through the BRIC National Competition and $642 million for Flood Mitigation Assistance (FMA) community-scale flood mitigation projects to help communities enhance their own resilience efforts. This funding will help communities large and small build resilience and prepare for future challenges.

This historic funding supported the following projects:
- Strengthening the Jefferson Parish, Louisiana, electrical grid to withstand 150 mph winds to decrease the risk of power outages to residents and critical facilities.
- Installing new sewer mains in Detroit’s Jefferson-Chalmers neighborhood to protect over 600 homes from flooding.
- Building three critical electrical hubs in Ko‘olaupoko, Hawaii, to keep the power on during severe weather and extended outages.
- Reducing extreme heat conditions in Portland, Oregon, by planting 10,500 trees over three years to reduce the impacts of heat islands, mitigate urban flooding during extreme rainfall events and improve air quality.
- Installing critical infrastructure upgrades to the Hobart Creek Reservoir Dam in Nevada to enhance safety and protect the water supply.
- Funding a new water pump station in Philadelphia to reduce flood risk and improve water quality and quality of life throughout the city.
- Improving storm drainage in Greenville, North Carolina, to reduce flood risk for 90 homes.
- Supporting a comprehensive wildfire mitigation program in Napa County, California, to provide long-term wildfire and climate resilience for residents and communities.
Of all the project selections, 64 use nature-based solutions to achieve program objectives, including funding for flood mitigation, wildfire, drought and extreme heat.


FEMA joined the Federal Buy Clean Initiative with 12 other federal agencies to tackle the climate crisis. FEMA’s funding of net-zero projects creates the opportunity to reduce utility costs, increase energy reliability and significantly reduce greenhouse gas pollution and climate-related hazard costs for communities. Examples of Net-Zero Energy projects already funded by FEMA include Blue Lake Rancheria Tribe’s Microgrid and the Newark Ironbound Resiliency Hub.
In addition, FEMA obligated more than $52 million to the first round of Flood Mitigation Assistance Swift Current funding to make homes safer and more resilient for National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) policyholders with repetitively and substantially flood-damaged properties. Swift Current aims to speed up the awarding of funding for flood mitigation assistance.
2 - Furthering Environmental Justice
FEMA has committed to the Justice40 Initiative, a government-wide program to ensure that historically underserved and overburdened communities receive the benefits of new and existing federal investments. The program aims to direct 40% of overall benefits from covered investments in specific sectors to communities identified as disadvantaged using the Screening Tool (CEJST).
Along with BRIC, FEMA’s Justice40 covered programs include the following:
- Flood Mitigation Assistance Grant Program.
- Regional Catastrophic Preparedness Grant Program.
- Risk Mapping, Assessment and Planning (Risk MAP) Program.
FEMA’s Grant Equity Threshold Tool (GETT) helps grant applicants meet the 40% threshold. With GETT, users can easily find out the percentage of the population living in a potential benefiting area who are in census tracts considered CEJST disadvantaged, designated as a Community Disaster Resilience Zone (CDRZ), and information about how they align with FEMA’s Community Resilience Challenges Index (CRCI). The tool also allows users to download files that can be included with grant application submissions.
This information allows us to examine equity and identify disadvantaged communities that have potential environmental justice concerns and greater challenges to resilience.

3 - Providing Technical Assistance
In 2023, FEMA responded to more than 100 new disasters, providing $1.3 billion in direct assistance to survivors. This included responding to the Maui wildfires, Typhoon Mawar in Guam, Hurricane Idalia and tornadoes in Mississippi and Arkansas. FEMA conducted geospatial damage assessments during response to Typhoon Mawar, helping the agency deliver critical disaster aid and assist teams on the ground with damage location information.
FEMA’s Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities Direct Technical Assistance (BRIC DTA) program provides tailored support to communities that may lack the resources to begin climate resilience planning and project solution design.

In its third year, the BRIC DTA program expanded the total number of entities benefiting from non-financial assistance to 74 communities, territories and Tribal Nations by announcing 46 additional selections, which include 20 Tribal Nations.
4 - Establishing Disaster Resilience Zones
On Sept. 6, 2023, FEMA announced the designation of 483 census tracts as Community Disaster Resilience Zones. The communities within these Zones will be eligible to receive targeted federal support to become more resilient to natural hazards and extreme weather worsened by the climate crisis.
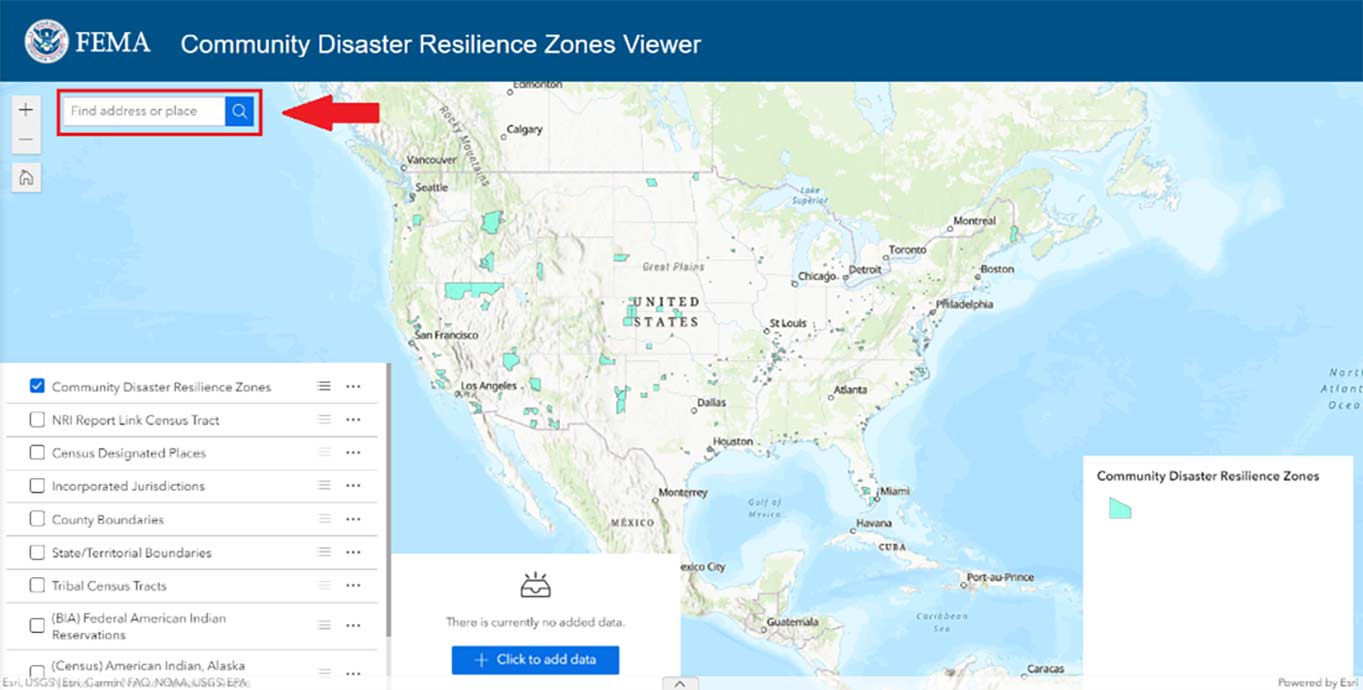
FEMA will use the Community Disaster Resilience Zones to focus on resilience activities and to encourage other federal agencies, the private sector, nonprofit and philanthropic organizations and private equity to invest in resilience projects.
In addition, FEMA has announced the first round of community disaster resilience zones across all 50 states and the District of Columbia, Tribal Nations and territories. These zones will help communities identify and address their unique resilience challenges, working towards a more sustainable future for all.
5 - Cultivating National Resilience
On April 23, FEMA will release the draft National Resilience Guidance for a 30-day public review and comment period. This national engagement period is an opportunity for the public to review the draft guidance and provide comment for FEMA’s consideration prior to finalizing the guide.
With the goal of increasing community and national resilience, the guidance:
- Promotes a common understanding of resilience.
- Emphasizes the critical relationship between chronic community stressors and shocks.
- Addresses the roles of all stakeholders.
- Provides an actionable approach to resilience planning and implementation.
- Incorporates a community resilience maturity model that walks through concrete steps to build resilience.
The guidance is available on National Resilience Guidance on FEMA.gov. FEMA will also host four 60-minute webinars to facilitate discussions and gather feedback from whole community partners to help improve the existing draft before finalizing the guide. Register at FEMA Events to learn more about how we can collectively make our nation more resilient.

To learn more about FEMA’s path forward to community climate resilience, visit goal two in FEMA’s Strategic Plan (2022-2026) on FEMA.gov.