This fact sheet describes the distinguishing features of attached garages versus enclosures used for parking, to help users understand where to record information on the FEMA Elevation Certificate form.
The FEMA Elevation Certificate (EC) form is used to collect and certify elevation information for structures. Data provided on the form is used to ensure compliance with the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) and community floodplain management regulations in the Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), to inform flood insurance premiums, and to support Letter of Map Change requests. When completing the EC form, users often have difficulty differentiating between an attached garage and an enclosure with a garage door. Table 1 illustrates how the flood zone and the garage’s designation as either an enclosure or an attached garage determines where elevation information should be entered on the form.
Table 1: Use of Elevation Certificate Fields by Flood Zone and Garage Designation
| Attached Garage | Enclosure | Basement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zones Where Base Flood Elevation (BFE) is Determined | Elevations in C2.d | Elevations in C2.a | Elevations in C2.a |
| Zone AO or A Without BFE | Measurements in E3 | Measurements in E1.a and E1.b | Measurements in E1.a and E1.b |
| All Zones, When Applicable | Area and flood openings in A9 | Area and flood openings in A8 | N/A |
Definitions
The following definitions are provided for the purposes of completing the Elevation Certificate. While other definitions of these features exist (e.g., NFIP Flood Insurance Manual, FEMA 480 NFIP Floodplain Management Requirements Desk Reference, local floodplain regulations), the definitions and descriptions in this fact sheet should be used as guidance when correctly filling out an EC form.
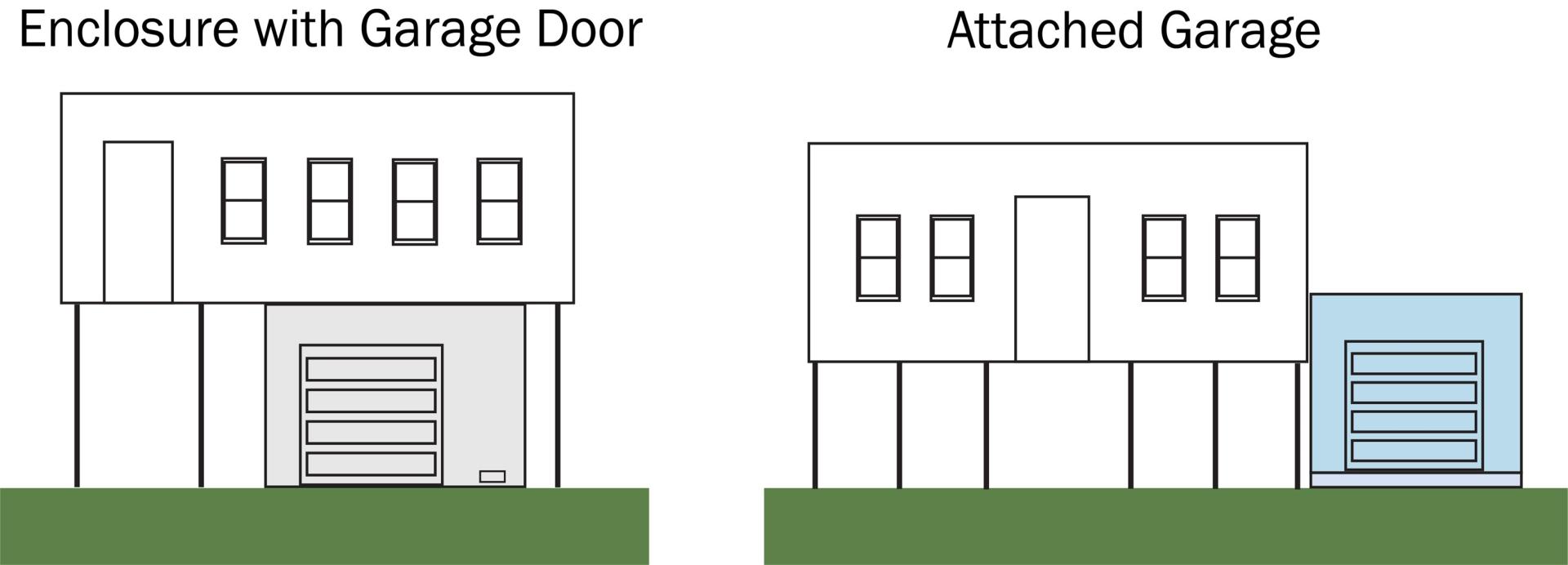
Attached Garage
An attached garage is an enclosed space used for parking that is adjacent to (beside or next to) the principal structure. This lateral extension of the primary structure is connected by either a common wall, a breezeway, a common roof, or a shared foundation. Attached garages may have the same or different floor elevations than living spaces or other enclosures, but may not be below ground level (grade) on all sides. If an enclosed space meets the definition of an attached garage, the presence of living space above it does not change this designation. Similarly, if an enclosed space meets the definition of an attached garage, the presence or absence of permanent flood openings does not change this determination.
The elevation of the attached garage (at its lowest point) should be recorded on the Elevation Certificate in C2.d for flood zones where a BFE is determined, or in E3 in Zones AO or A without BFEs. Information about the square footage of the attached garage and any permanent flood openings should be recorded in A9.
Enclosure
An enclosure is an enclosed space used primarily for parking, limited storage, or building access, that is directly underneath (or mostly underneath) the lowest living floor or principal use of the building, for both single and dual foundations. An enclosure with a garage door can have the same or different floor elevation than living spaces or other enclosures. Note that areas used for parking, storage, or access to the building, that are below grade on all sides, are also considered basements.
The elevation of the enclosure floor (at its lowest point) should be recorded on the Elevation Certificate in C2.a for flood zones where a BFE is determined, or in E1.a and E1.b for Zones AO or A without a BFE. Information about the square footage of the enclosure and any permanent flood openings should be recorded in A8.
The presence or absence of flood openings has no impact on the designation of the space as an attached garage or enclosure used for parking. However, the presence of sufficient permanent flood openings may change whether the floor of the attached garage or parking enclosure is interpreted as the building’s lowest floor for floodplain management compliance purposes. An enclosure used for parking with or without permanent flood openings is recorded in A8. An attached garage with or without permanent flood openings is recorded in A9.
Basement
A basement is any area of the building, including (but not limited to) any sunken room, sunken portion of a room, or garage area having its floor below ground level (subgrade) on all sides. Spaces that are subgrade on all sides and beneath the principal use of an elevated building, such as an underground garage, may be considered both an enclosure and a basement. The elevation of the basement floor (at its lowest point) should be recorded on the Elevation Certificate in C2.a for flood zones where a BFE is determined, or in E1.a and E1.b for Zones AO or A without a BFE.
Below-grade parking garages are only allowed beneath non-residential buildings in Zones A1-30, AE, AH, and AO. Certification of dry floodproofing must also be provided. See FEMA Technical Bulletin 6 for more detailed guidance.
Examples of Attached Garages and Parking Enclosures
The following pages include example photographs and illustrations of buildings with various foundation types. Please note this is not meant to be an exhaustive list, but rather to describe several common structure types and the distinguishing features that would result in a garage area being classified as either an enclosure used for parking or as an attached garage.
Non-Elevated Foundation Types
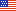
SLAB ON GRADE (NON-ELEVATED) WITH ATTACHED GARAGE
In the example shown in Figure 1, the garage is located on the same slab or raised-slab foundation as the rest of the structure to which it is connected. The garage is adjacent to the principal structure and is considered an attached garage. Note that the presence of living space above the garage does not change its designation.
An attached garage may be connected to the main structure by a common wall, a common roof, a shared foundation, or a breezeway (Figure 2). The attached garage designation would also apply to a split-level building, where the garage is adjacent to the principal structure, and all of the floors are at or above the lowest adjacent grade.
If any floor in a split-level structure is below grade on all sides, it would be considered a basement foundation (see next set of examples). The location of the parking area in such a split-level structure informs whether it is an attached garage or an enclosure with a garage door.
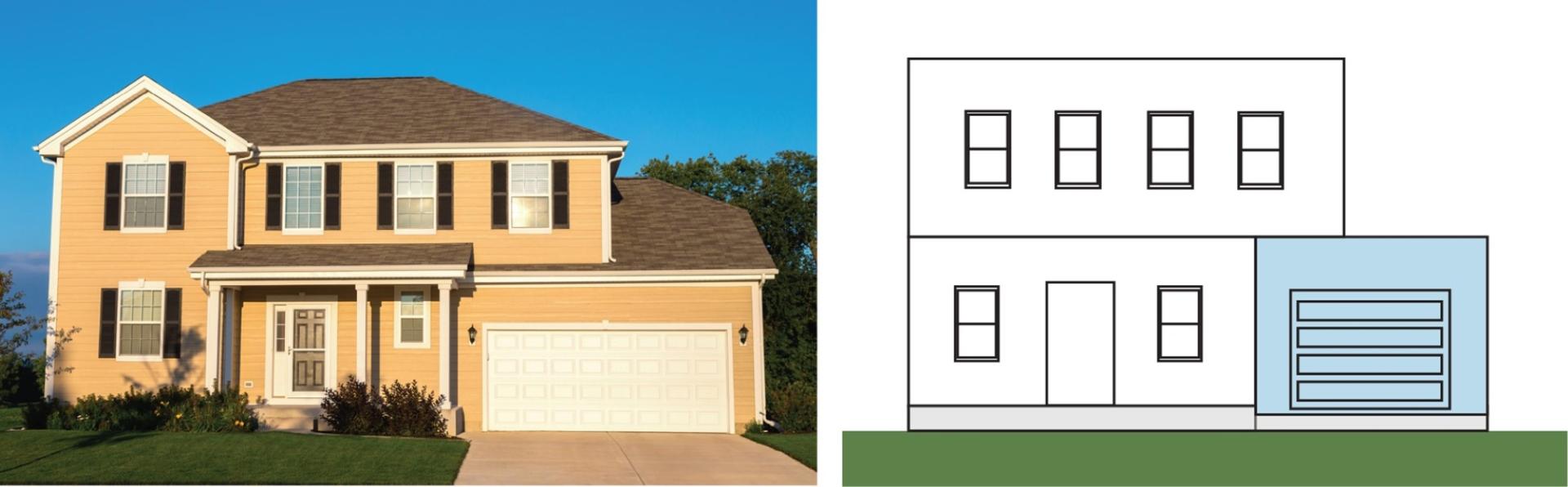
BASEMENT (NON-ELEVATED) WITH ATTACHED GARAGE
In the example shown in Figure 3, the bottom floor of the structure is a basement area that is below grade on all sides. The garage is located adjacent to the structure’s next higher floor. Since the garage is adjacent to the principal structure, it is considered an attached garage. This attached garage is connected to the main structure by a shared foundation with common walls and roof; an attached garage may also be connected by a breezeway. Note that the presence of living space above a garage does not change its designation.
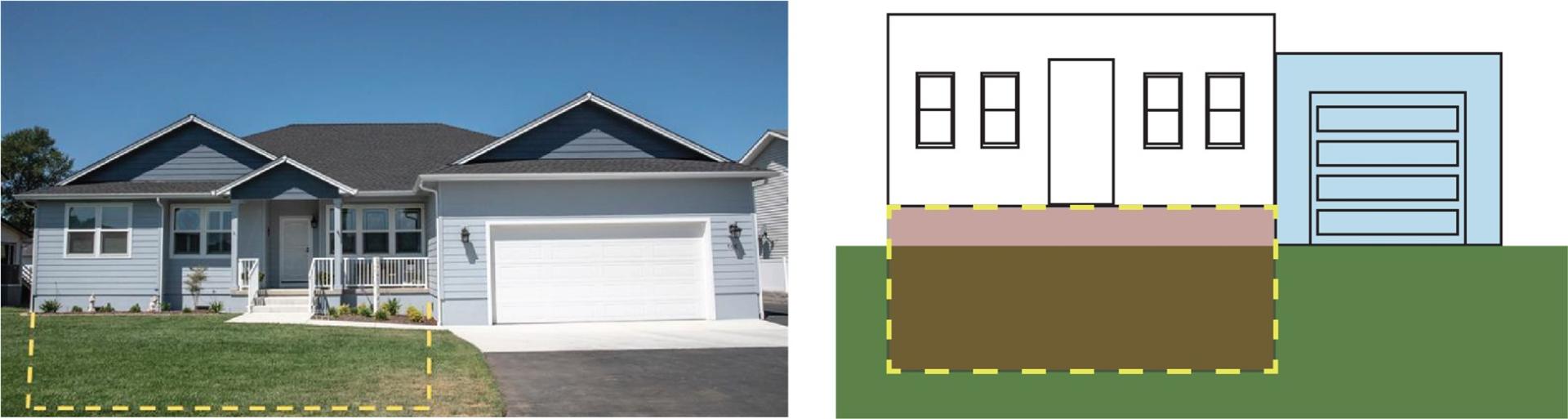
This attached garage designation would also apply to a split-level building where the bottom floor is a below-grade area (basement), and the parking area is at or above grade on at least one side (Figure 4). The garage is adjacent to the principal structure and is considered an attached garage.
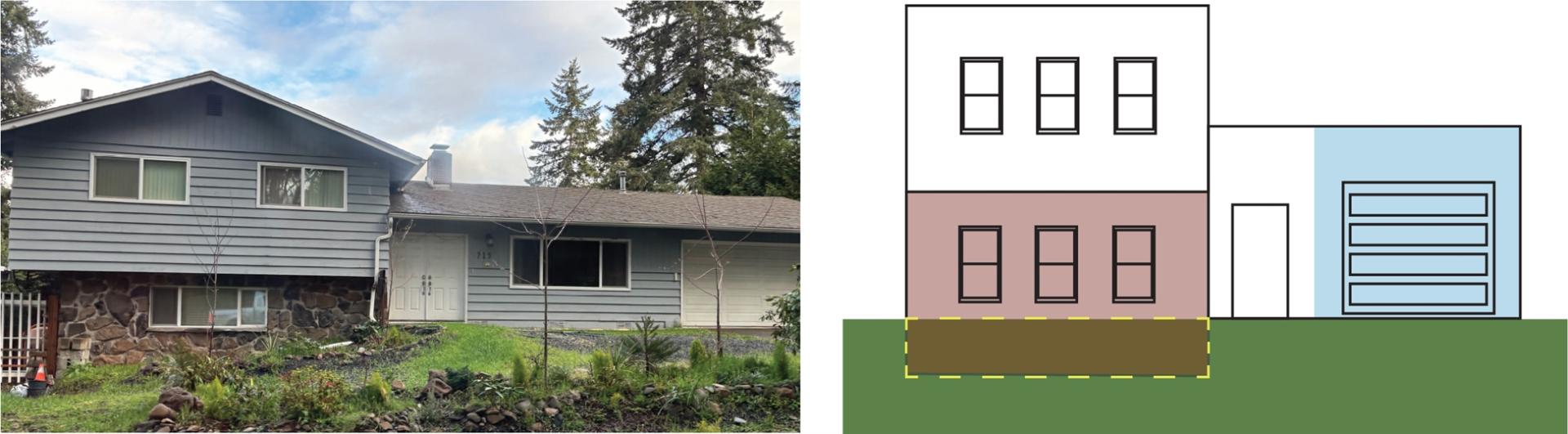
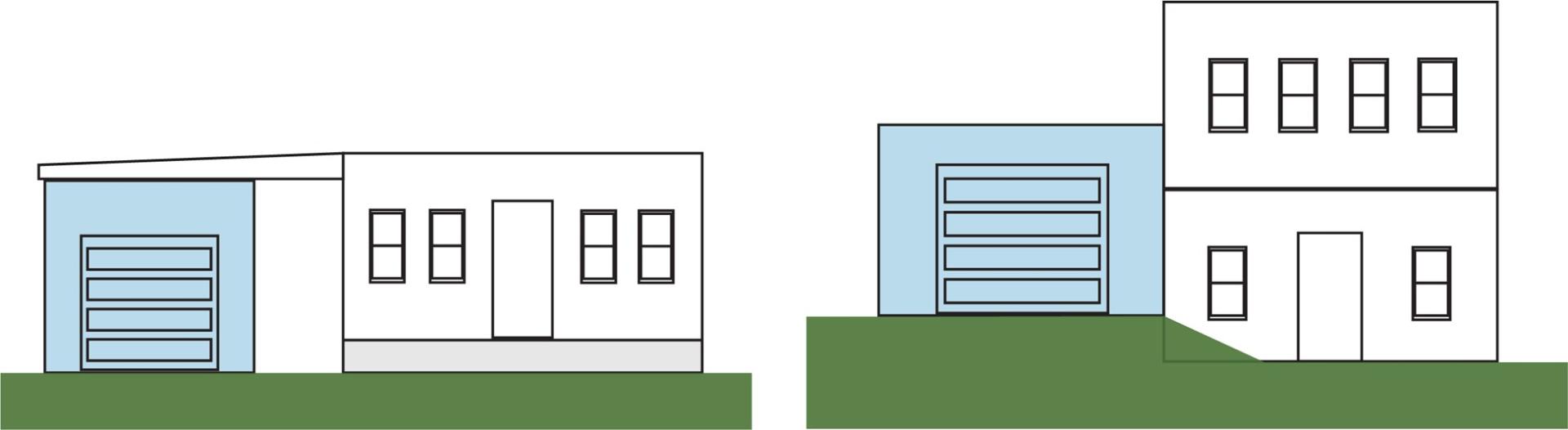
BASEMENT (NON-ELEVATED) WITH ENCLOSURE USED FOR PARKING
The example structure in Figure 5 has a garage that is below grade on all sides, and that is located underneath the lowest living floor of the structure. A floor that is below ground level (grade) on all sides is considered a basement. Therefore, this parking area is considered a basement enclosure.
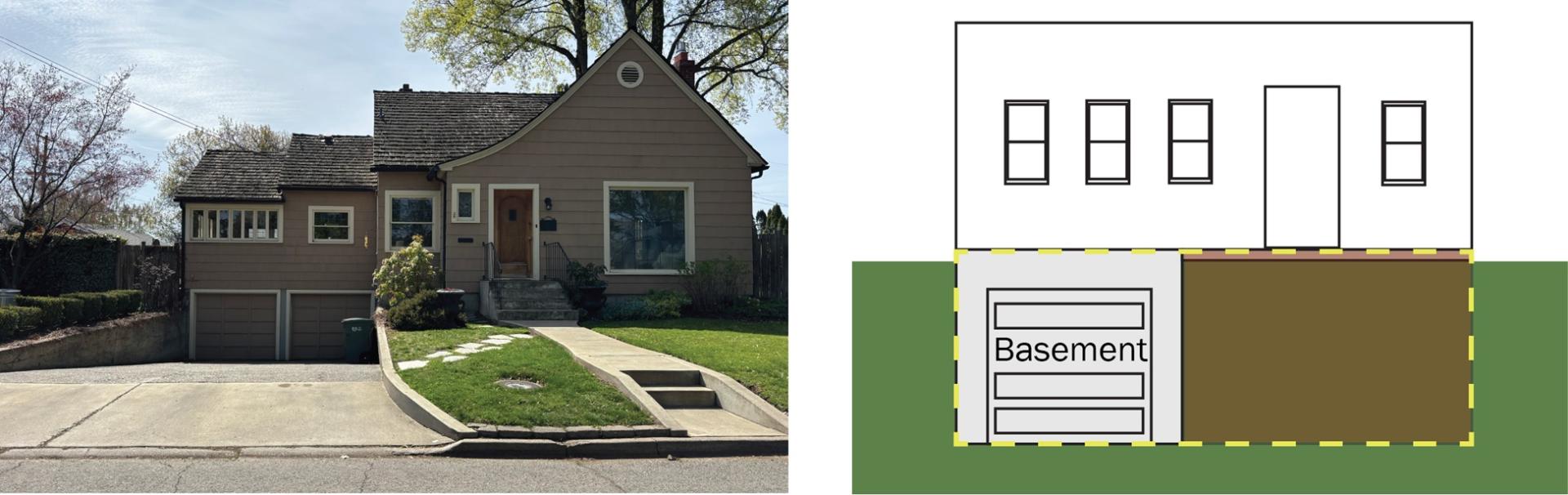
This designation of basement enclosure would also apply to a non-elevated split-level building, where the floor of the enclosed area used for parking is below grade on all sides and located underneath the lowest living floor of the structure.
Elevated Foundation Types
ELEVATED ON CRAWLSPACE (INCLUDING SUB-GRADE CRAWLSPACES), WITH ATTACHED GARAGE
In the example shown in Figure 6, the structure is elevated on a crawlspace that is not a full story high (5 feet or less from the bottom floor to the next higher floor). The garage is located adjacent to the principal structure, as a lateral extension of the primary living floor. Therefore, it is considered an attached garage.
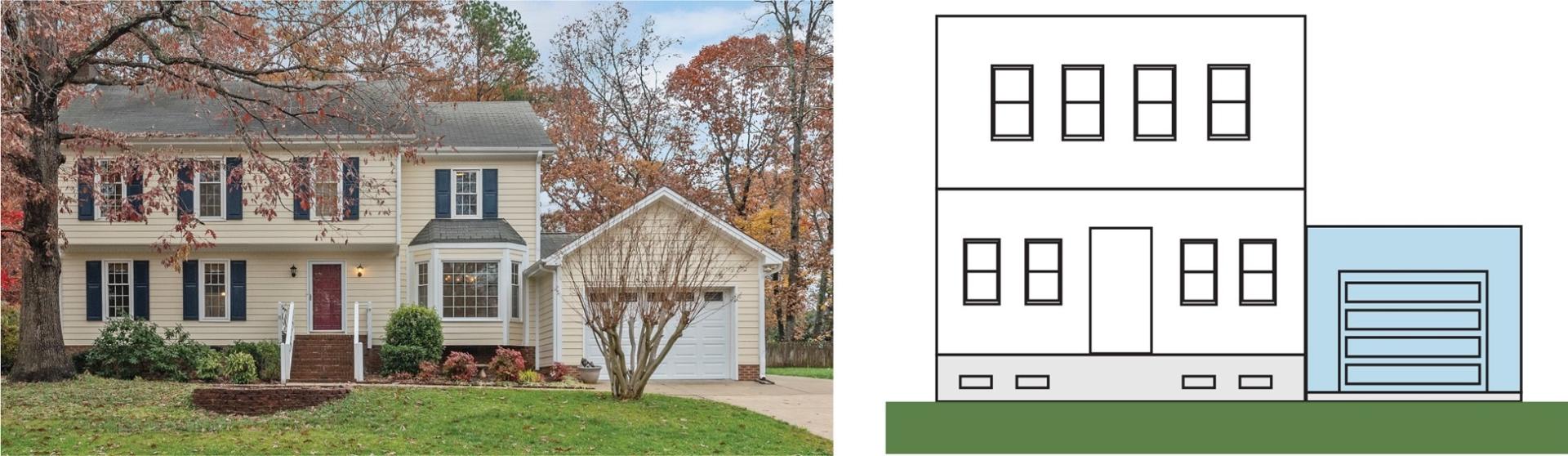
Figures 6 and 7 show scenarios where both A8 and A9 will be completed on the EC form. Information about the square footage of the crawlspace enclosure will be recorded in A8, and information about the square footage and any flood openings of the attached garage will be recorded in A9.
ELEVATED WITH ENCLOSURE ON SOLID FOUNDATION WALLS, WITH ATTACHED GARAGE
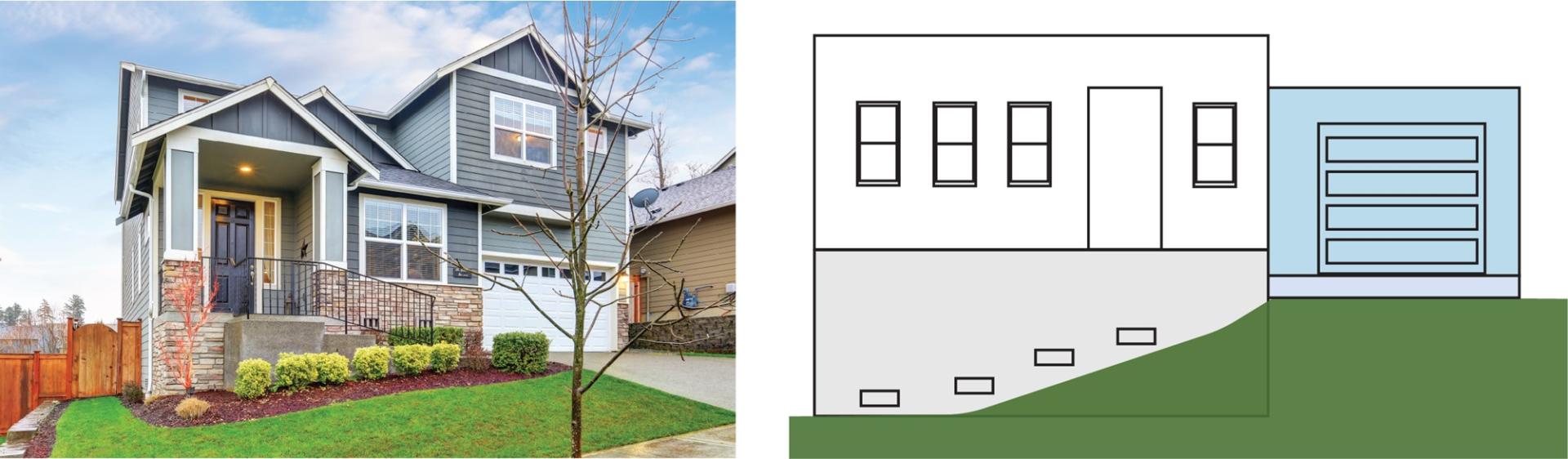
The example structure in Figure 7 is elevated on a full-story enclosure (greater than 5 feet) with solid foundation walls. The garage is located higher than the building’s bottom floor (unfinished enclosure floor), and adjacent to the elevated living floor of the building. This is considered an attached garage. Note that the presence of living space above the attached garage does not change its designation.
ELEVATED WITH ENCLOSURE ON SOLID FOUNDATION WALLS, WITH PARKING AREA IN THE ENCLOSURE
The example structure in Figure 8 is elevated on full-story (greater than 5 feet) solid masonry foundation walls. The bottom floor of the structure is the garage, which is located directly underneath the principal use of the building on the next higher elevated floor. Therefore, this parking area is considered an enclosure, not an attached garage. The presence or absence of flood openings in the walls does not impact this designation. A garage door is not considered a flood opening.
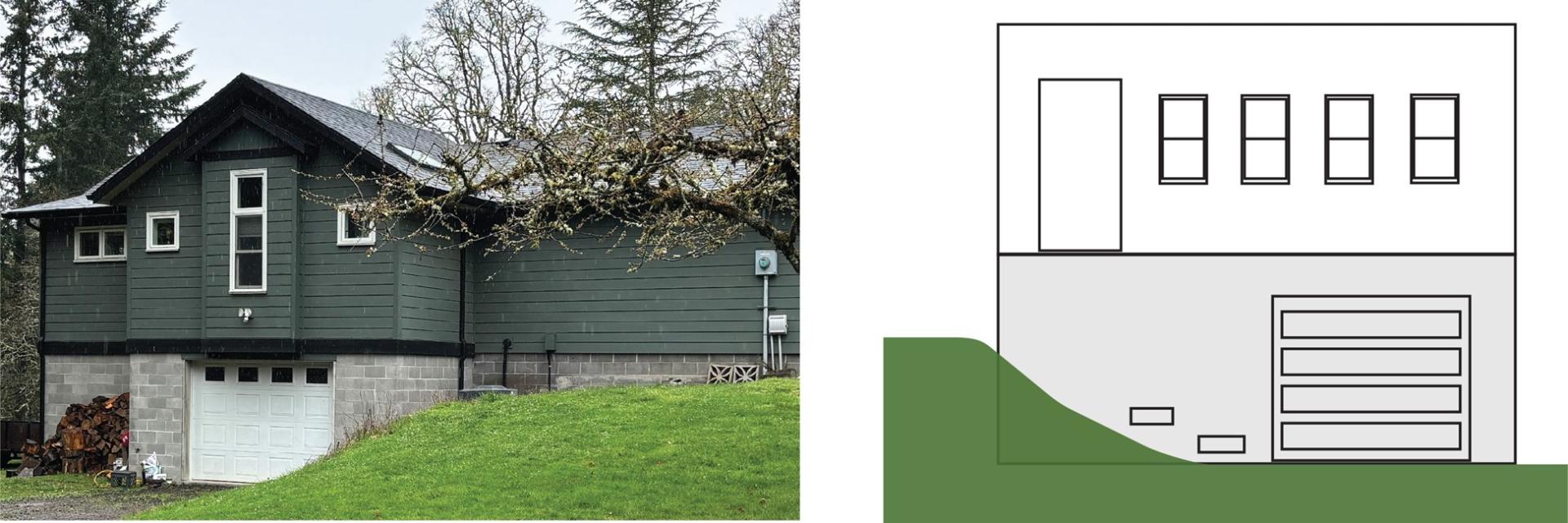
Elevated on Posts, Piles, Piers, Columns or Parallel Shear Walls
Structures elevated on posts, piles, piers, columns, or parallel shear walls are common in coastal areas and throughout the country. If a structure with this foundation type has the garage underneath the principal use of the building (Figure 9), it is considered an enclosure. The walls of the enclosure used for parking would typically be breakaway or shear walls, not load-bearing foundation walls.
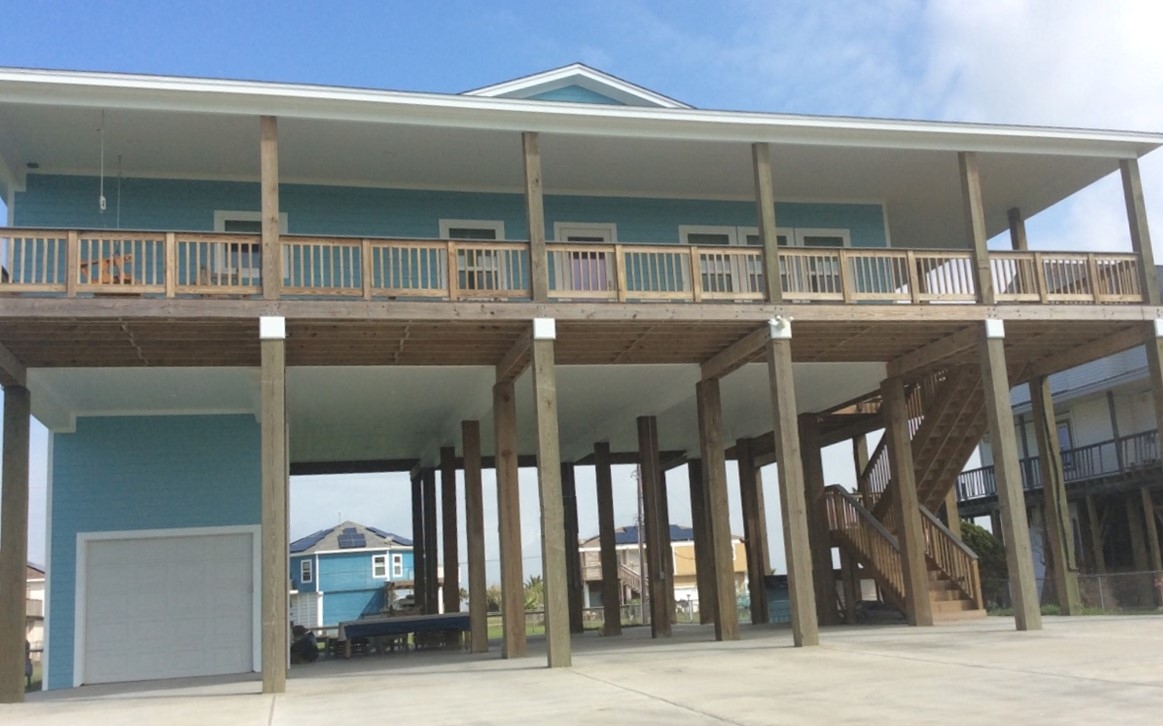

In structures with this foundation type, walled parking areas with a garage door are most often enclosures, not attached garages. Record information about the square footage of an enclosure used for parking and any permanent flood openings in A8 of the EC form.
For the garage of a structure on pier, post, or pile construction to instead be considered an attached garage, it must be a lateral extension of the primary structure (see Figure 10). As a lateral extension, the attached garage may have a different foundation type than the main structure (e.g., raised slab on grade, slab on stem wall, solid foundation walls) if allowable in the flood zone where the building is located.
Conclusion
Attached garages and enclosures used for parking are features that need to be clearly identified for determining a structure’s compliance with local floodplain regulations and NFIP elevation requirements. Care should be taken to ensure the EC form is filled out in a way that most accurately represents a structure’s features. When in doubt, provide clarifying information in the Section D or F Comments boxes.
If the Garage Designation is Unclear, Use the Comments Box and Take Photographs
There may be scenarios where it is unclear whether a structure’s parking area is an attached garage or an enclosure. For example, the building may have a dual foundation, or other unique attributes.
In these circumstances, enter the elevations into the EC form to the best of your ability. Use the Comments box in Section D for zones where a BFE is determined, or in Section F for Zone AO and A without a BFE, to add any additional details and describe the features of the structure. Attach extra photographs to the EC form for clarification as necessary, so that reviewers can properly assess the structure for compliance and insurance purposes.
Additional Information
For more information, contact your local floodplain administrator or your local flood insurance agent. For additional questions about the EC form, visit www.fema.gov or email nfipunderwritingmailbox@fema.dhs.gov. For specific questions about the Community Rating System (CRS) program, email the CRS team at fema-crs@fema.dhs.gov.
Download the current version of the FEMA Elevation Certificate form at: https://www.fema.gov/flood-insurance/find-form/underwriting